Biodiversity Research and Monitoring
The Biodiversity Research section is responsible for monitoring the health of the ecosystem by surveying key species, using camera traps and other survey methods, in collaboration with villagers, key district partners, and national and international researchers.
Biodiversity monitoring has three main objectives:
• Provide baseline data on wildlife population and threats to set quantitative management targets
• Facilitate assessments of whether wildlife populations and threats are increasing, decreasing or remaining stable
• Conduct research on several aspects of biodiversity to inform conservation action and advance scientific knowledge
What is a target species for monitoring?
Target species that:
• are vulnerable to key threats
• have the potential to respond to effective management efforts
• are not so rare that it is impossible to collect sufficient data to monitor trends
Wildlife Surveys in Nakai Nam Theun National Park
Camera-trap Surveys: Special cameras that take photos of anything passing by are set in the forest for a period of a few weeks or months. Photos of wildlife are later counted
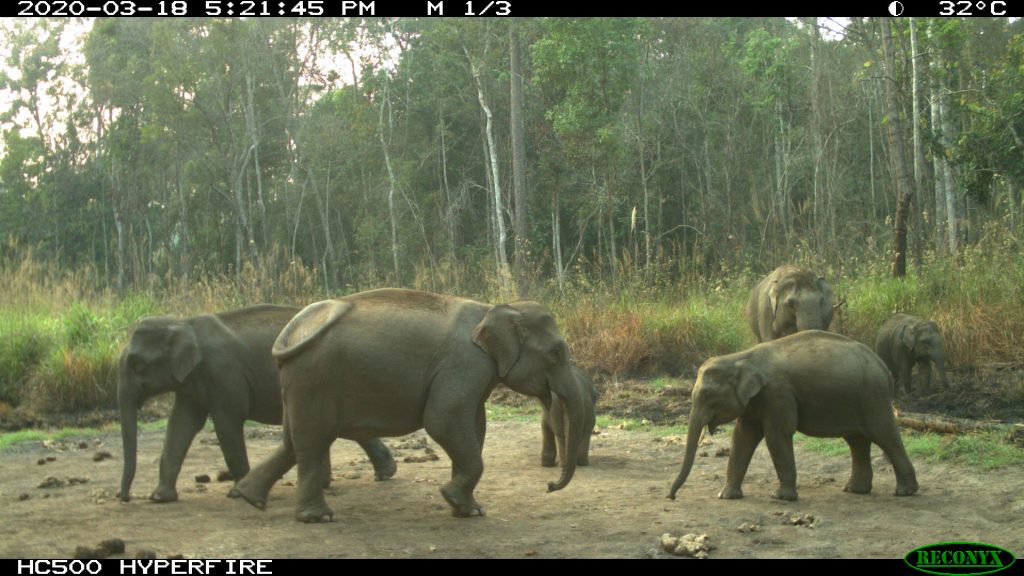
Elephants, Ungulates, Bears, and Pangolins
The park has an estimated population of elephants of more than 100 individuals. Other notable mammal species include Sambar Deer, Gaur, Chinese Serow, two spe- cies of bear, Asian Black Bear and Sun Bear, two species of pangolins, Sunda Pangolin and Chinese Pangolin.


 Users Today : 45
Users Today : 45 Users Yesterday : 29
Users Yesterday : 29 This Month : 601
This Month : 601 This Year : 6590
This Year : 6590 Total Users : 9010
Total Users : 9010